

The \(y\)-intercept is \(1\) units right of the axis of symmetry, \(x=-1\). Find the point symmetric to the \(y\)-intercept across the axis of symmetry.įind the \(y\)-intercept by finding \(f(0)\). The axis of symmetry is the line \(x=-1\). Since \(a=2\), the parabola opens upward. x(x4) 25 Explanation for Standard Form for Quadratic Equation in Math.

Example for Standard Form for Quadratic Equation in Math. The standard form of quadratic equation is written as Ax 2 + Bx + C 0. Step 1: Determine whether the parabola opens upward or downward. Standard Form for Quadratic Equation in Math. The graph of the quadratic function is in the form of a parabola. However, there are also other ways of describing everything about a parabola that may be a bit more intuitive.+3\) by using its properties The standard form of the quadratic function is f(x) ax 2 +bx+c where a 0. To completely describe any parabola, all someone needs to tell you are these three values. These three values, a, b, and c, will describe a unique parabola. How would you describe the effect that changing the value of b has on the graph? If you wish to explore this behavior in a bit more depth, you may use this applet. In addition, the cone consisting of all tangents from a fixed point to a quadratic surface cuts every plane in a conic section, and the points of contact of. A quadratic surface intersects every plane in a (proper or degenerate) conic section. In mathematics, a quadratic form is a polynomial with terms all of degree two ('form' is another name for a homogeneous polynomial).For example, + is a quadratic form in the variables x and y.The coefficients usually belong to a fixed field K, such as the real or complex numbers, and one speaks of a quadratic form over K. Note what happens to the graph when you set a to a negative value.Ĭ shifts (translates) the graph vertically.ī alters the the graph in a complex way. Notes Standard form of a quadratic equation is yax2+bx+c, where a is not 0 Vertex form of a quadratic equation is ya(x-h)2+k, where (h,k) is the vertex of. A second-order algebraic surface given by the general equation (1) Quadratic surfaces are also called quadrics, and there are 17 standard-form types. It determines how much the graph is stretched away from, or compressed towards, the x-axis.
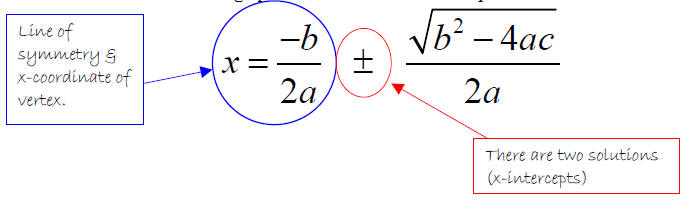
This is much more challenging!Ī is referred to as the "dilation factor". We can rewrite it as 3 x 2 + 12 x 63 3x2+12x-63 3 x 2 + 1 2 x 6 3 3, x, squared, plus, 12, x, minus, 63 and then proceed through the checklist. the vertex of the graph (the blue point labelled V) passes through the blue point on the graph: (-3, -1). This quadratic expression is not currently in standard form. some part of the graph passes through the blue point on the graph: (-3, -1) the graph becomes a horizontal line, or opens down the vertex lies to the right, or left, of the y-axis Then substitute in the values of a, b, c. Directions: Using the digits 1 to 9 at most one time each, fill in the boxes to create a quadratic equation with. ax2 + bx + c 0 2x2 + 9x 5 0 a 2, b 9, c 5. Maximum Value of a Quadratic in Standard Form. The standard form of a quadratic function is f(x) a(x h)2 + k. The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) ax2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. Solution: Step 1: Write the quadratic equation in standard form. A quadratic function is a function of degree two. Once you have a feel for the effect that each slider has, see if you can adjust the sliders so that: Solve by using the Quadratic Formula: 2x2 + 9x 5 0.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
